Elements of Art Principles of Design Components of Art
Have y'all e'er wondered what the building blocks of a painting are? Whether you wait at a Renaissance masterpiece like the Mona Lisa (c. 1503) or an Impressionist en Plein air slice by Claude Monet, you volition exist confronted with a visual composition of a scene or person, which is really a combination of artistic elements and principles. In this commodity, we will explain what these elements of art and principles of design are.
Tabular array of Contents
- one The Fundamentals: What Are the Principles of Art?
- 2 The 7 Elements of Art
- 2.1 Colour
- 2.two Value
- 2.iii Line
- ii.4 Form
- two.5 Shape
- two.half dozen Space
- 2.vii Texture
- iii The Principles of Art
- 3.one Residuum
- iii.ii Dissimilarity and Emphasis
- iii.3 Movement and Rhythm
- 3.four Variety
- 3.v Unity and Harmony
- three.6 Pattern and Repetition
- three.7 Proportion
- 3.8 Scale
- iv Bringing It All Together
- 5 Oftentimes Asked Questions
- v.1 What Are the Principles of Pattern?
- 5.ii What Is the Difference Betwixt the Elements of Art and the Principles of Design?
- five.3 What Are the 7 Principles of Art?
The Fundamentals: What Are the Principles of Fine art?
According to the Merriam-Webster Online Lexicon, the give-and-take "principle" means: "a comprehensive and key constabulary, doctrine, or assumption", including "a rule or code of comport". Therefore, a principle refers to the fundamental aspects or rules of something.
In the visual arts, it would refer to its fundamentals or rules, which leads us to the question, what are the fundamentals of visual arts, or what are the principles of art? A set of rules that artists follow that informs the limerick? Often, these are as well criteria used to clarify artworks.
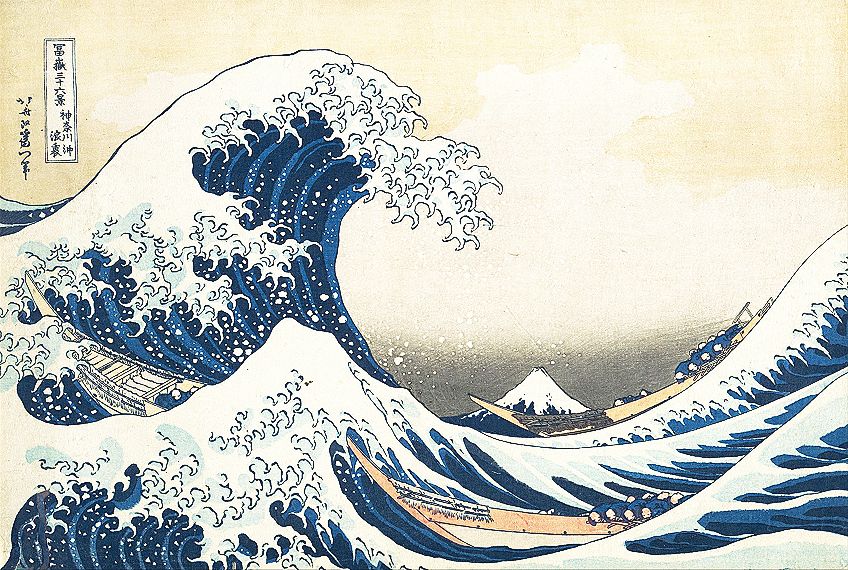 The Great Wave off Kanagawa (between 1830 and 1832) by Katsushika Hokusai, located in the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City, United States; Katsushika Hokusai, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The Great Wave off Kanagawa (between 1830 and 1832) by Katsushika Hokusai, located in the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City, United States; Katsushika Hokusai, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Information technology is important to note before nosotros explore these art principles, that these should not exist confused with the elements of art, which are described as the "visual tools" that compose an artwork. These also become criteria past which artworks are analyzed. We will also look at these in more detail below.
Furthermore, you may come up beyond various fine art sources that apply these ii terms (elements and principles) interchangeably.
Therefore keep it in heed while you do art reading and research, and remember their differences and functions inside the visual arts. We volition aim to provide the differences between the two while too intentionally applying the terms interchangeably.
The Vii Elements of Art
| Fine art Element | Characteristics | Artwork Examples |
| Color | We encounter color equally reflected calorie-free that bounces off objects effectually united states of america. Color has three characteristics: hue, value, and intensity. There are primary, secondary, and 3rd colors on the colour wheel. | Composition VII (1913) by Wassily Kandinsky |
| Course | Form is three-dimensional with book, which includes elevation, depth, and width. It includes shapes like cubes, spheres, and cones. Forms can either be organic or geometric. | David (1501 to 1504) past Michelangelo Galatea of the Spheres (1952) past Salvador Dalí |
| Line | There are vertical, horizontal, and diagonal lines. Lines can exist thick, thin, curved, directly, or patterned to emphasize a shape. | The Starry Night (1889) by Vincent van Gogh Composition with Crimson, Yellow, and Bluish (1929) by Piet Mondrian |
| Value | Value is the lightness or darkness of a color. Also referred to as "luminosity". | Melancholy I (1514) by Albrecht Dürer |
| Shape | Shape is two-dimensional and has width and length. It includes circles, squares, rectangles, or pyramids. Shapes can be organic or geometric. | Three Musicians (1921) by Pablo Picasso Black Square (1915) by Kazimir Malevich |
| Space | Space is the altitude between or around objects. Space can be positive or negative, open up or closed. Infinite also portrays perspective and depth. | The Hunters in the Snow (1565) by Pieter Brueghel the Elder Chair (Cannes) (1961) past Pablo Picasso |
| Texture | Texture refers to the "surface quality" of an artwork. Texture tin can either be felt in real life or portrayed through the illusion of information technology past using paint or other media. | Penitent Magdalene (1453 to 1455) by Donatello The Arnolfini Portrait (1434) by Jan van Eyck |
Allow us start with the seven elements of art. Every bit we explained above, these are the "visual tools" used to etch a painting. Think of them as the colors on your palette, every bit each one offers a unique quality, which gives your composition its shape, so to say.
There are seven elements of fine art, namely, colour, form, line, value, shape, space, and texture. These are important to empathise when viewing a painting, or creating a painting. We will go through each of these in more than item beneath.
Color
Color is an important chemical element in visual arts considering information technology creates meaning effects, not only visually, but psychologically too. There is a scientific discipline to color and many neat artists accept celebrated the inherent magic of color likewise, just think nigh Wassily Kandinsky or Piet Mondrian, to name a few.
Colour offers a wide spectrum, so let usa commencement outset with how it works with light considering this will provide some context when we side by side expect at an artwork. Color reaches our optics in the form of reflected light, which "bounces" off the objects around us.
There are iii chief aspects or elements related to color, namely, hue, value, and intensity (this is too sometimes referred to as saturation or chroma). Hue relates to the color of the color, so to say, for instance, the hue is blue, green, or purple.
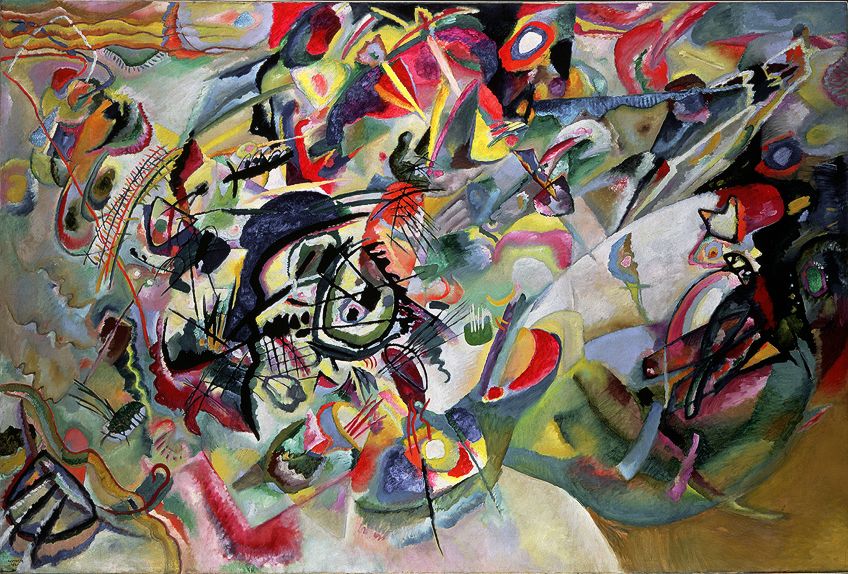 Composition VII(1913) by Wassily Kandinsky, located in the Tretyakov Gallery in Moscow, Russia; Wassily Kandinsky, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Composition VII(1913) by Wassily Kandinsky, located in the Tretyakov Gallery in Moscow, Russia; Wassily Kandinsky, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Value relates to the "lightness" of colour; its lightness like white or its darkness like black, and all the other colors in between. If a white is added to a color information technology becomes known as a "tint" and the value of it becomes lighter, and conversely, if black is added to a color it becomes a "shade" and the value becomes darker.
Intensity relates to how brilliant or dull a color appears. This can frequently be dislocated with value too, just the distinguishing cistron between the two is that intensity otherwise referred to as saturation, refers to the brightness of the color. Notwithstanding, if the value of the color is lighter the intensity of the color will besides decrease and vice versa.
The color bike is some other of import attribute and includes the primary, secondary, and tertiary colors. The chief colors consist of red, blue, and xanthous and the secondary colors consist of purple, orangish, and green.
 Color Study: Squares with Concentric Circles (1913) by Wassily Kandinsky, located in the Stadtische Galerie in Munich, Federal republic of germany; Wassily Kandinsky, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Color Study: Squares with Concentric Circles (1913) by Wassily Kandinsky, located in the Stadtische Galerie in Munich, Federal republic of germany; Wassily Kandinsky, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The colors betwixt main and secondary colors are referred to as "intermediary" colors, namely, yellow-light-green, xanthous-orangish, carmine-orange, red-purple / violet, blue-green, and bluish-majestic/violet. It is important to notation here that these intermediary colors are likewise sometimes called tertiary colors.
However, several online sources state that tertiary colors are, in fact, the combination of two secondary colors and not the intermediary colors, which are a combination of primary and secondary colors, evident on the colour wheel.
Value
Value is some other chemical element of fine art closely connected to colour. As we mentioned above, value refers to the lightness and darkness of whatever color. Another term that relates to value is as well "luminosity". For a better agreement of how value really works, you lot tin can view an prototype on a grayscale, in which, there will exist lighter and darker areas.
This gives an indication of the lighter and darker areas of color. Another term utilized here is "contrast", which refers to the difference between the lighter and darker areas.
 Melencolia I(1514) by Albrecht Dürer, located in the Minneapolis Institute of Art in Minneapolis, Us; Albrecht Dürer, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Melencolia I(1514) by Albrecht Dürer, located in the Minneapolis Institute of Art in Minneapolis, Us; Albrecht Dürer, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Line
Line in visual art is considered 1 of the more important elements and, by paraphrasing, information technology is typically described as a mark that moves in space between 2 points. There are dissimilar types of lines, namely, vertical, horizontal, and diagonal.
Lines can also appear thick, thin, curved, directly, short, long, or patterned, which creates varying furnishings in a composition.
 Composition 2 in Crimson, Blueish, and Yellow(1930) by Piet Mondrian, located in the Kunsthaus Zürich in Zürich, Switzerland; Piet Mondrian, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Composition 2 in Crimson, Blueish, and Yellow(1930) by Piet Mondrian, located in the Kunsthaus Zürich in Zürich, Switzerland; Piet Mondrian, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
For example, motion, depth, shading, perspective, equally well as emphasizing a shape or "profile" can be created with line. This is visible if we look at examples of artists who applied thick nighttime outlines to shapes from the Expressionism art movement.
Some notable artists who made use of thick lines are Edvard Munch and Vincent van Gogh.
Form
Form every bit an art element refers to the three-dimensionality of an object, it is usually described as having volume, which comprises width, acme, and depth. Information technology is also represented through other elements like color variations and lines to indicate a contour or outline.
Furthermore, in visual fine art, nosotros are generally looking at a two-dimensional surface, therefore a course creates the "illusion" of three-dimensionality.
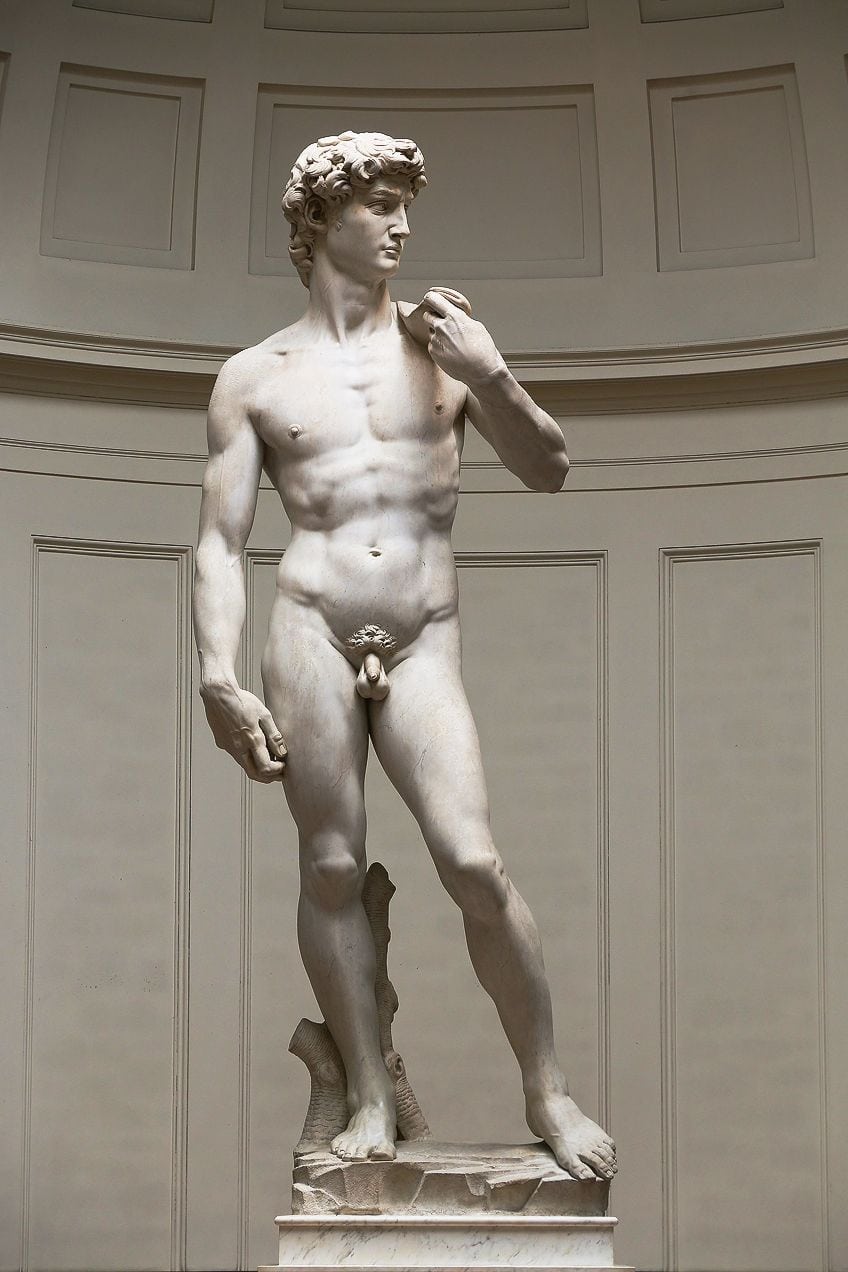 David(1501 – 1504) by Michelangelo, located in the Galleria dell' Accademia in Florence, Italy; Michelangelo, CC Past-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
David(1501 – 1504) by Michelangelo, located in the Galleria dell' Accademia in Florence, Italy; Michelangelo, CC Past-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
There are different types of forms, namely, organic, and geometric forms. Organic forms can originate from nature and are more random and asymmetrical; geometric forms are described as "mathematical", namely, the cylinder, cube, cone, or pyramid, and sphere.
Shape
Shape relates closely to form, simply the main difference is that a shape refers to ii-dimensionality. Information technology is often described as "flat", with simply length and width, and does not have the same appearance of volume that a form has. Similarly, shapes can also be grouped nether the categories, geometric or organic.
Shape gives the contour of an object, which essentially comprises lines.
 Black Square(1915) past Kazimir Malevich, located in the Tretyakov Gallery in Moscow, Russian federation; Kazimir Malevich , Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Black Square(1915) past Kazimir Malevich, located in the Tretyakov Gallery in Moscow, Russian federation; Kazimir Malevich , Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
There are unlike types of shapes, namely, circle, square, triangle, rectangle, oval, and others. A fun fact about these shapes is when they plough into forms, for case, a circle becomes a sphere, a triangle becomes a cone, and a square becomes a cube, and and then forth.
Some other artistic technique that conveys shapes is using positive and negative infinite.
Space
Infinite is often described as the "altitude" either "inside", "around", or "betwixt" the compositional space, which tin can exist a canvass, a sculptural infinite, or whatever other form of art. There are also different types of space, namely, positive, negative, and open and closed space.
Positive space is the object or subject itself in artwork, for example, if a pair of scissors is drawn, the positive space would be the pair of scissors. The negative space is the space around the subject, in this case, the pair of scissors and the expanse in the loops of the scissors would constitute the negative infinite.
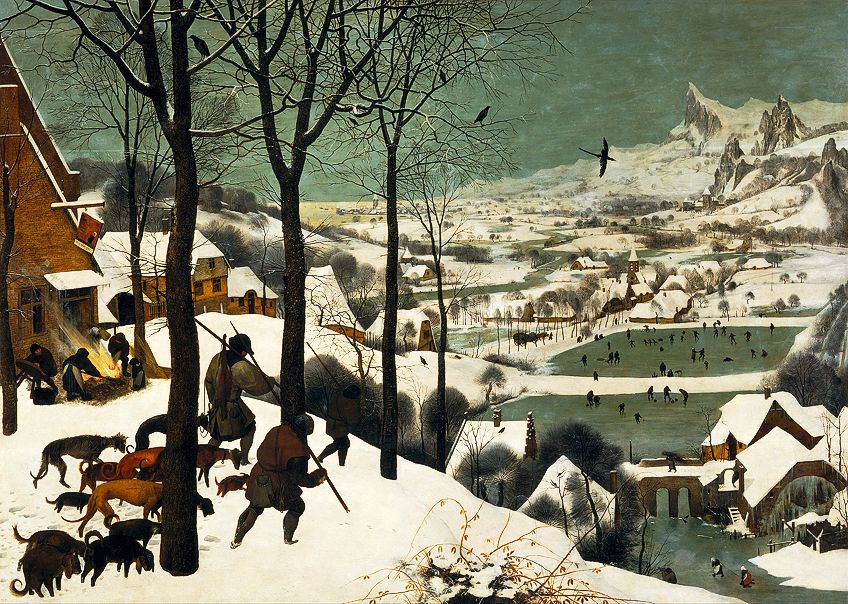 The Hunters in the Snow(1565) past Pieter Brueghel the Elder, located in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, Republic of austria; Pieter Brueghel the Elder, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The Hunters in the Snow(1565) past Pieter Brueghel the Elder, located in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, Republic of austria; Pieter Brueghel the Elder, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
This is like open and closed spaces, where the object would be in the airtight space and the open infinite would be effectually it. Space is also conveyed when a composition is separated into parts, peculiarly when yous analyze a painting and describe the subject matter in terms of its spatial arrangements, which can either be in the foreground, heart ground, or background, upper, lower, left, or right.
Additionally, space is conveyed in art through variations of depth, otherwise referred to every bit perspective, and proportion otherwise referred to by size.
Texture
Texture is all virtually feeling, and at that place are typically ii primary ways it is conveyed in visual art, namely, in real life, or three-dimensional space, for instance, sculptures or the "tactile" feeling of pigment on a canvass, for example through the "impasto" technique, where the paint is physically textured on the sheet.
The other way that texture tin be shown is through suggestion or the "illusion" of texture on a two-dimensional infinite.
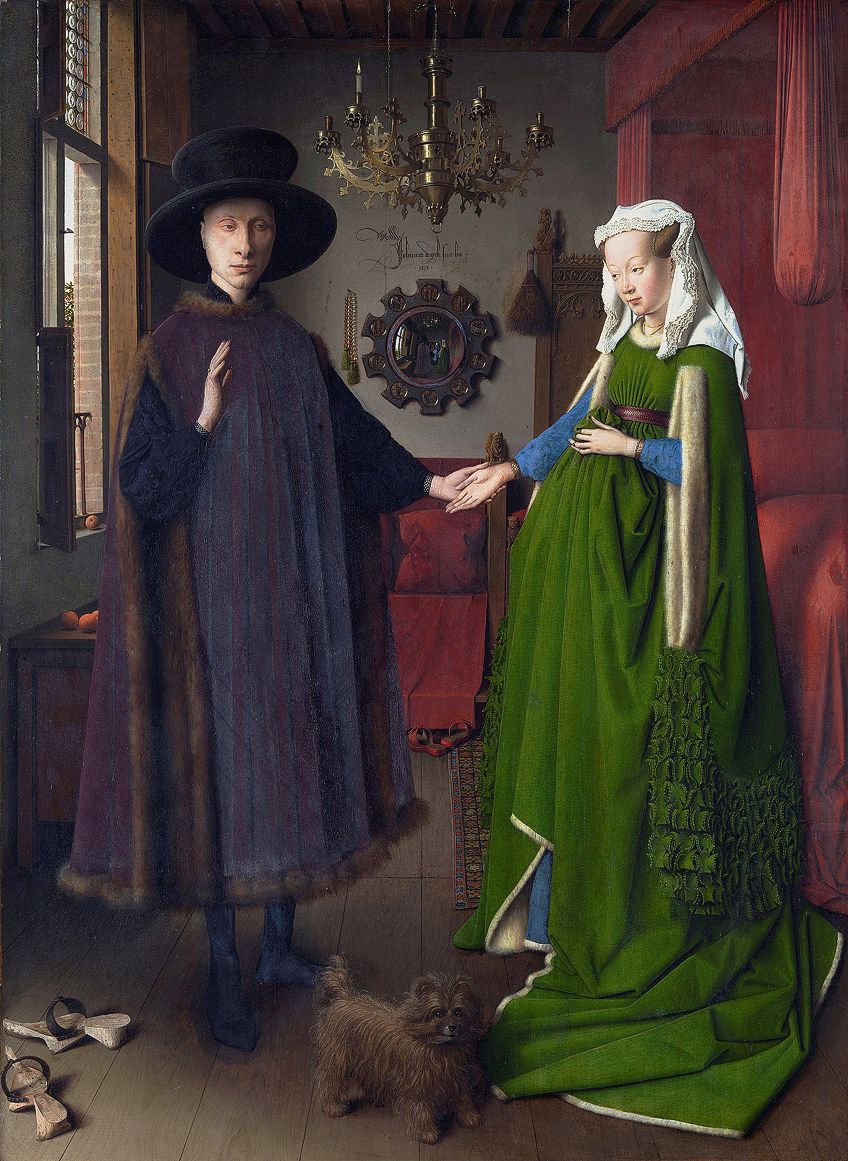 The Arnolfini Portrait (1434) past January van Eyck, located in the National Gallery in London, United Kingdom;Jan van Eyck, Public domain, via Wikimedia Eatables
The Arnolfini Portrait (1434) past January van Eyck, located in the National Gallery in London, United Kingdom;Jan van Eyck, Public domain, via Wikimedia Eatables
This is done past utilizing various techniques with paint, pencil, or pen on a canvas or piece of paper. Both refer to what is described every bit the "surface quality" of an artwork. Texture gives character to an art form and creates psychological effects for us, the viewers when we engage with it.
The Principles of Art
| Art Principle | Characteristics | Artwork Example |
| Balance | Residuum can be symmetrical, asymmetrical, or radial. | The Concluding Supper (c. 1495 to 1498) by Leonardo da Vinci |
| Dissimilarity and Accent | Contrast is created by placing different art elements together to add accent, this can also exist through light/dark effects. | The Calling of Saint Matthew (1599 to 1600) past Caravaggio |
| Move and Rhythm | Movement creates action or dynamic effects to atomic number 82 the viewers' eyes to the focal point. Rhythm is created through repeated elements and this creates movement. | The Great Wave (1830 to 1832) past Katsushika Hokusai The Scream (1893) by Edvard Munch |
| Multifariousness | Variety creates an ongoing interest in a composition, it is the utilization of various fine art elements similar colour, line, or texture. | Haystacks (1891) by Claude Monet |
| Unity and Harmony | Unity refers to the completeness of the limerick and all the elements working together to create a unified whole. Harmony is like to unity but information technology can also mean the reverse of variety. | A Sunday on La Grande Jatte (1884) past Georges Seurat |
| Pattern and Repetition | Art elements are placed in patterned arrangements to create an effect. | Golconda (1953) by René Magritte |
| Proportion | How an object's parts relate to each other in size. | The Vitruvian Human (1490) by Leonardo da Vinci |
| Calibration | The size of the bailiwick/object compared to the residuum of the objects in the composition. | Cristina's Globe (1948) by Andrew Wyeth |
Nosotros at present have an understanding of the elements of art, which nosotros described equally about beingness like the colors on your palette. The question, "what are the principles of pattern?" direct relates to the elements of art, and as we go through the principles of pattern in fine art, we volition see how these determine the artwork'due south overall issue. These could almost be seen in your paintbrushes, so to say; each paintbrush will be unique, providing a specific function to bring the composition together.
In that location are several principles of design in art, some sources explore it equally 10, while others come across information technology as half dozen or seven. Some tin can also be grouped together as the concepts are like, but it should be noted not to be confused past the close similarities of some.
Nosotros will outline viii art principles below, with some grouped together, and a brief explanation of each. These are, namely, balance, contrast/emphasis, movement, rhythm, variety, unity/harmony, design/repetition, proportion, and scale.
We accept separate articles for each principle of fine art:
- Motion in Art
- Emphasis in Fine art
- Unity in Art
- Rhythm in Fine art
- Texture in Art
- Proportion in Art
- Residuum in Art
- Harmony in Fine art
Remainder
Balance is nearly the compositional "weight of visual elements", whether these are practical in such a manner that provides the consequence of even distribution. There can exist symmetrical, asymmetrical, and radial residual.
Symmetrical refers to both sides being the same, or "mirroring" 1 some other. Asymmetrical refers to both sides having unlike subject field thing or objects, but at that place is a balanced effect, nonetheless. Radial balance ways that the visual elements are "equally" placed effectually a centralized "betoken" in the composition.
 The Terminal Supper(1495 – 1498) past Leonardo da Vinci, located in the Santa Maria delle Grazie in Milan, Italy; Leonardo da Vinci, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The Terminal Supper(1495 – 1498) past Leonardo da Vinci, located in the Santa Maria delle Grazie in Milan, Italy; Leonardo da Vinci, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Contrast and Accent
Contrast refers to the placements of unlike elements in a composition, for example, colour, space, shape, or others. By utilizing contrast strategically, it will convey a sense of emphasis, or otherwise stated; it will emphasize a certain area in the composition.
Emphasis refers to a "focal betoken" in a composition.
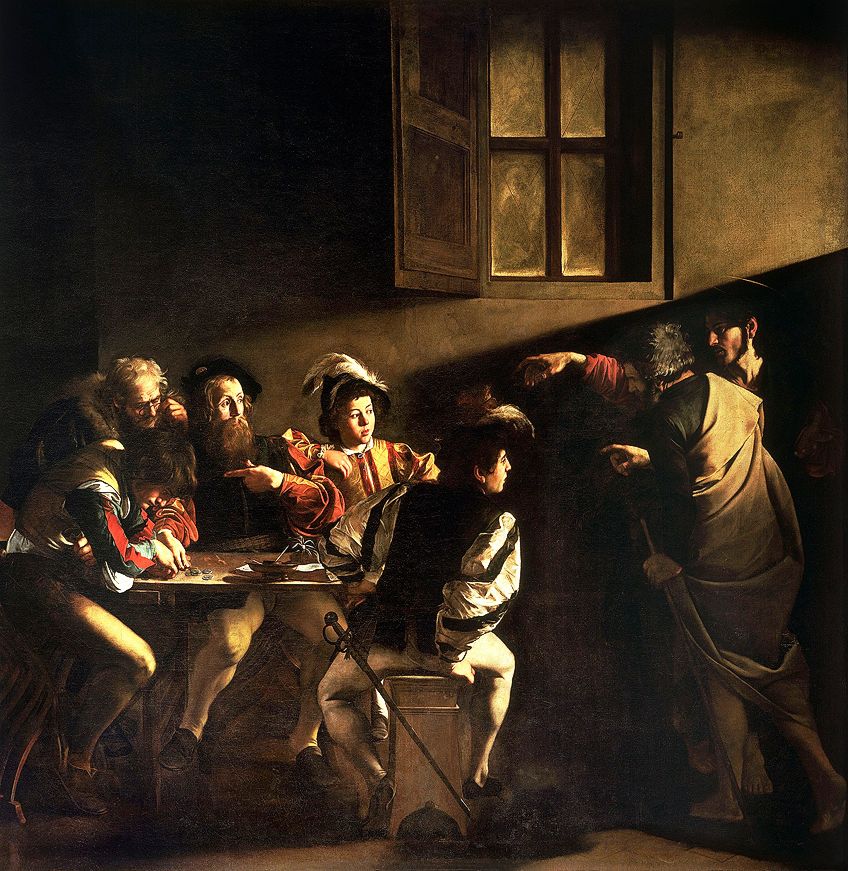 The Calling of Saint Matthew (1599 – 1600) by Caravaggio, located in Contarelli Chapel in Rome, Italy;Caravaggio , Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The Calling of Saint Matthew (1599 – 1600) by Caravaggio, located in Contarelli Chapel in Rome, Italy;Caravaggio , Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Movement and Rhythm
Movement is all about leading the eye to the focal point or central discipline, or simply around the entirety of the limerick. It is achieved by arranging and applying various elements in such a fashion that creates a sense of dynamism.
Some of the art elements that create movement can be the placement of different lines.
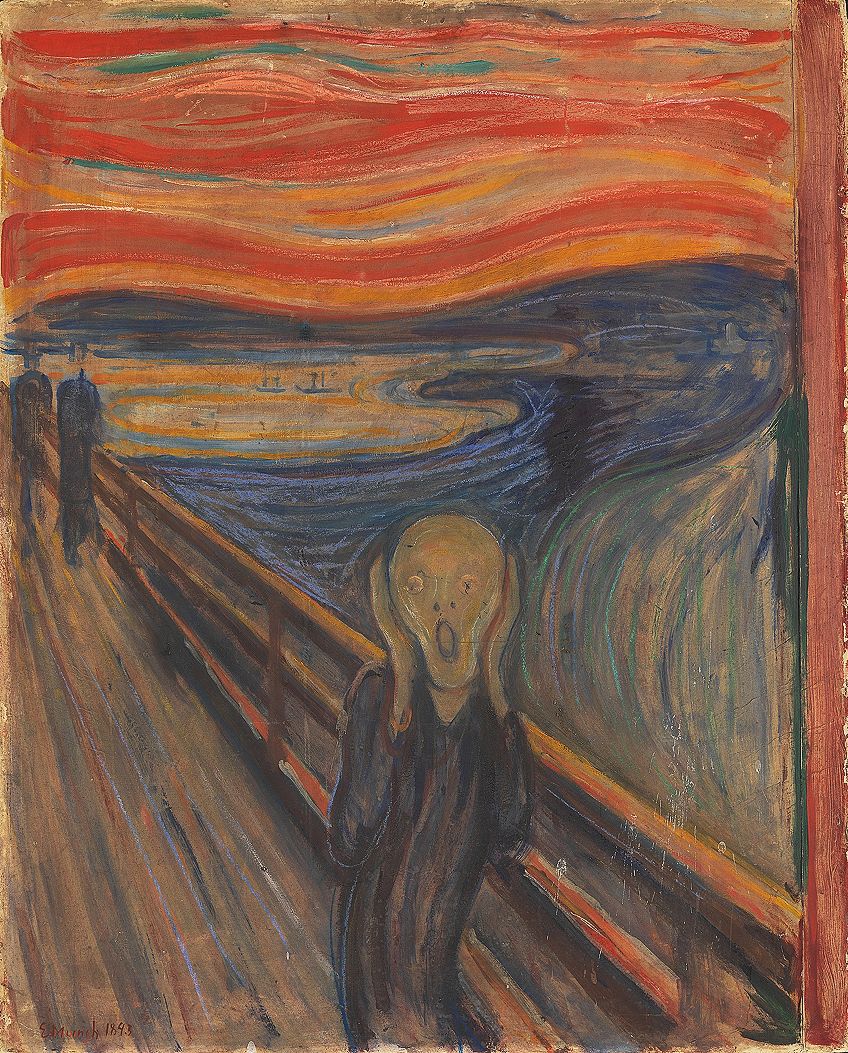 The Scream(1893) by Edvard Munch, located in the National Museum of Art, Compages, and Design in Oslo, Norway; Edvard Munch, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The Scream(1893) by Edvard Munch, located in the National Museum of Art, Compages, and Design in Oslo, Norway; Edvard Munch, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
These lines are usually diagonal or curved, which add together to the color, infinite, shape, and diverse other elements. Rhythm is mainly created through repeating elements or placing them in patterned arrangements.
This ultimately creates a sense of movement in a limerick.
Variety
Diversity is basically most unlike elements in a composition that gives it its uniqueness. It provides a continuing dissimilarity, or some sources describe "anarchy", which engages the viewer and maintains a level of interest and awe for the composition; it evokes emotion and expression.
Importantly, diversity also needs to be utilized in a balanced manner so as not to create too much of information technology that it detracts from the composition's beauty or narrative, or too little that it creates a sense of boredom or confusion in pregnant.
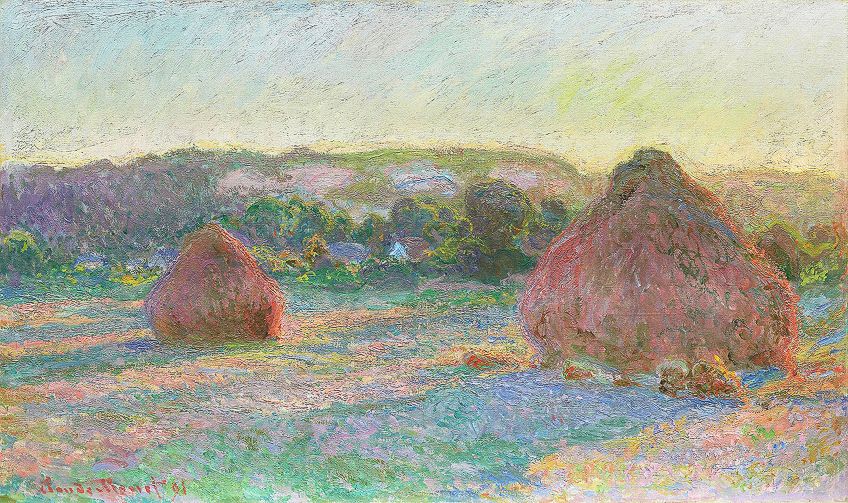 Stacks of Wheat (End of Summer)(betwixt 1891 and 1897) by Claude Monet, located in the Art Institute of Chicago in Chicago, Us;Claude Monet, Public domain, via Wikimedia Eatables
Stacks of Wheat (End of Summer)(betwixt 1891 and 1897) by Claude Monet, located in the Art Institute of Chicago in Chicago, Us;Claude Monet, Public domain, via Wikimedia Eatables
Unity and Harmony
Although this principle might seem like Balance, there is a slight departure in its implications. Both terms, unity, and harmony, can be viewed similarly and differently, which tin make information technology confusing.
If we expect at their similarities, both tin refer to how all the visual elements in a composition work together, so to say. In other words, are all the visual elements complementing each other? Are there disordered visual elements?
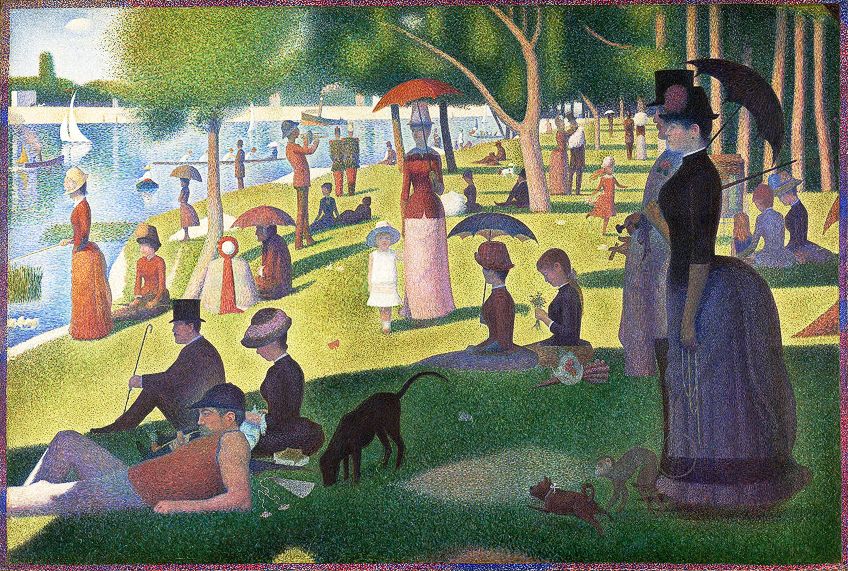 A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte(betwixt 1884 and 1886) by Georges Seurat, located in the Art Institute of Chicago in Chicago, Us;Georges Seurat, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte(betwixt 1884 and 1886) by Georges Seurat, located in the Art Institute of Chicago in Chicago, Us;Georges Seurat, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
What can set the terms autonomously is that Harmony relates to how art elements are used in conjunction, which can be through repetition or rhythm, ultimately information technology is the opposite of Variety and the idea of chaos, information technology provides a feeling of "calm" or "flow".
Unity can also be described equally relating to the entire compositional coherence, whether you apply principles of diversity and harmony.
Pattern and Repetition
Patterns are art elements placed in repeated arrangements or sequences, whether these are from lines, colors, shapes, or others. This repetition in a composition can create various furnishings, for instance, the idea of move, texture, unity, or balance.
Proportion
Proportion refers to how an object'south parts in a limerick relate to each other due to their size or shape, for example, a figure'due south eye can be in proportion to the rest of his or her face, it can also be too small or also large.
This will either create emphasis or unlike visual effects.
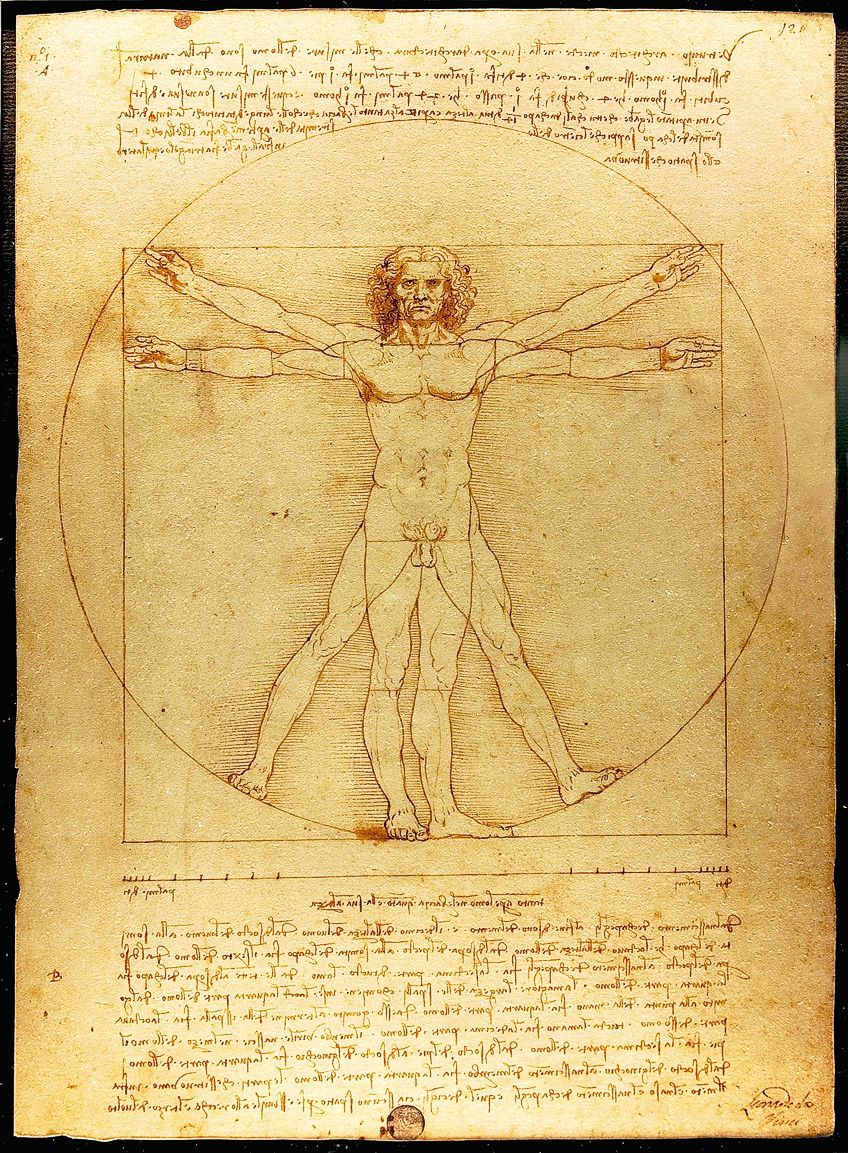 Vitruvian Man(c. 1492) by Leonardo da Vinci, located in the Gallerie dell' Accademia in Venice, Italy;Leonardo da Vinci, Public domain, via Wikimedia Eatables
Vitruvian Man(c. 1492) by Leonardo da Vinci, located in the Gallerie dell' Accademia in Venice, Italy;Leonardo da Vinci, Public domain, via Wikimedia Eatables
Scale
In the principles of design in fine art, it is important not to confuse scale with proportion. Calibration relates to the object's size within the limerick compared to all the other objects. For example, a figure standing adjacent to a building, which volition be to scale if depicted accurately in terms of how information technology would announced in real life or as some fine art sources state, "typically the size of the artwork to the viewer's body".
Bringing It All Together
In the article above nosotros explore the 7 principles of art, which we have noted is too referred to as the element of art. However, it is important to call back the difference between the elements of art and principles of design, and so to say.
The elements of art can exist viewed as the colors on your palette, and the principles of design can be viewed as the different paintbrushes. When applying each color, or art element, with a specific paintbrush, or fine art principle, y'all will create a compositional whole.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Principles of Design?
There are several principles of design in art, which can all exist applied to create certain visual furnishings and feelings. These are balance, contrast/emphasis, movement, pattern/repetition, proportion, rhythm, scale, unity/harmony, and variety.
What Is the Departure Between the Elements of Art and the Principles of Pattern?
The elements of art and the principles of design are different, merely sometimes the terms are used interchangeably. The elements of art are described equally visual tools for creative compositions, and the principles of design in art are all nearly how these elements are utilized.
What Are the Seven Principles of Art?
There are usually 7 elements of art. These have been described in different ways; some sources refer to them as the building blocks for creative compositions while other sources have described these as the visual tools utilized to create compositions. These are as follows: color, class, line, texture, shape, space, and value.
Source: https://artincontext.org/principles-of-art/
0 Response to "Elements of Art Principles of Design Components of Art"
Post a Comment